Converting Methods: Slitting with Industrial Razor Blades
Types of razor slitting technique, industrial slitting blades
What is razor slitting in industrial converting? Razor slitting is a cutting method where a sharp, stationary razor blade is positioned across a moving web of material. It is the most economical and precise technique for slitting thin films, foils, laminates, and label stock into narrow rolls. Razor slitting is simple to set up, delivers straight, dust-free edges, and is widely used in flexible packaging and plastic film converting. While it has limits on thick or abrasive webs, it remains the go-to choice for light-gauge films where edge quality and speed are essential. In industrial web converting, slitting is a core operation used to convert rolled material webs into narrower rolls. Three primary slitting methods dominate the process: shear cutting, score / crush cutting and razor slitting. This article focuses on razor slitting and explores its technical implementation, advantages, and industrial razor blade options.
Content:
- What is razor slitting?
- Types of razor slitting technique
- What are the advantages of the razor slitting method?
- What kind of blades are used for razor slitting?
- Industrial razor blades for film and foil slitters
- Coated industrial razor blades
- Which industrial razor blade fits my goals?
What is razor slitting and how does it work?

Razor slitting is an industrial cutting method where a sharp, stationary industrial razor blade is positioned across the path of the moving web in a slitter machine. As the material passes the slitter blade, it is cut by direct contact. The resulting cut depends on the characteristics of the web material. These include thickness, density, stiffness, ductility, coating, and other factors. When razor slitting, the material is unwound from the roll, passed through the razor blades, cut in air or in a grooved roll, and finally wound onto cores called spools or bobbins.
This technique is commonly used for thin plastic films, where clean, straight cuts are required. Razor slitting is often chosen for its simplicity, low cost, and ability to produce narrow cuts with minimal waste.
However, razor cutting has some limitations. It may not be suitable for thicker or tougher materials, and the blades may require frequent replacement due to wear and tear. The optimal range is between 0.5 and 7 mils (approximately 12 to 175 microns), depending on film type and slitting razor blade quality. While razor slitting can technically cut paper or filled films, blade wear occurs rapidly, making such use cases less practical or economical. Additionally, the process might produce dust or debris, which requires careful removal to prevent contamination or other issues. Despite its speed and wear limitations, razor slitting remains one of the most practical and economical slitting methods. It’s ideal for converters handling flexible packaging, label films, and light laminates.
Which applications use razor slitting?
 Razor slitting is often used for high-speed cutting of thin and flexible materials and fits best for slitting and converting packaging plastic films, aluminium foil, non-woven materials.
Razor slitting is often used for high-speed cutting of thin and flexible materials and fits best for slitting and converting packaging plastic films, aluminium foil, non-woven materials.
Most razor slitting applications involve materials like polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), biaxially-oriented polypropylene (BOPP), PET, laminates, and tape. It's used extensively in the flexible packaging and label industries, particularly for slit widths ranging from edge trims to multiple narrow lanes across the web. While it’s not ideal for thick or abrasive webs, razor slitting is perfect for high-speed converting lines producing light-gauge film products.
Blade Holding Systems and Web Support Methods
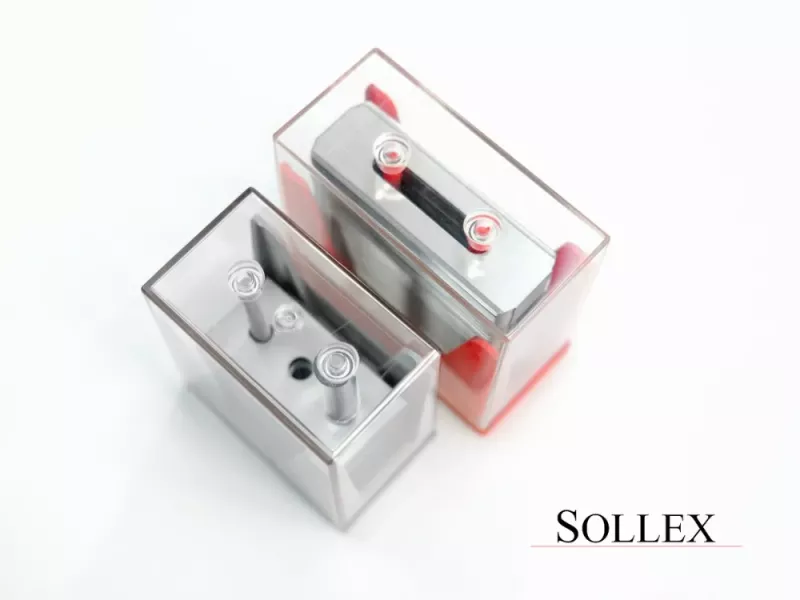
Razor Blade in a Holder
 There are several options used to hold and adjust razor blades in slitting systems, each offering different levels of precision and flexibility. The most basic approach involves individual holders, where each blade is mounted independently. This allows for fast repositioning and is often used for edge trims or broader slit widths. However, the physical size of the holders limits how closely blades can be placed.
There are several options used to hold and adjust razor blades in slitting systems, each offering different levels of precision and flexibility. The most basic approach involves individual holders, where each blade is mounted independently. This allows for fast repositioning and is often used for edge trims or broader slit widths. However, the physical size of the holders limits how closely blades can be placed.
Razor blades are mounted at an angle in razor blade holders to slit the moving web. The angle of the blade is important because it affects the quality of the cut. If the angle is too shallow, the material may tear or become jagged. If the angle is too steep, the blade may cause excessive friction and wear out quickly.
Razor Blade Block
A more precise method is the block and blade system. In this setup, multiple blades are positioned between spacers within a fixed block. This preassembled block allows for faster machine setup, tighter slit tolerances, and repeatable results. Operators benefit from the increased exposure of the blade edge, which permits multiple cutting positions as the blade wears. This system is ideal for narrow slitting applications, such as 3–4 mm wide lanes, where individual holders would be too bulky.
Razor Blade Comb
Another practical configuration is the razor comb, where blades are dropped into pre-slotted comb patterns. These combs come in fixed spacing (e.g. 25 mm or 1 inch), and are ideal for repetitive production with standard widths. They offer extremely fast setup and are often used in environments with high job change frequency. Many converters maintain both metric and imperial combs to cover a wider range of jobs.
What web support methods are used in razor slitting?
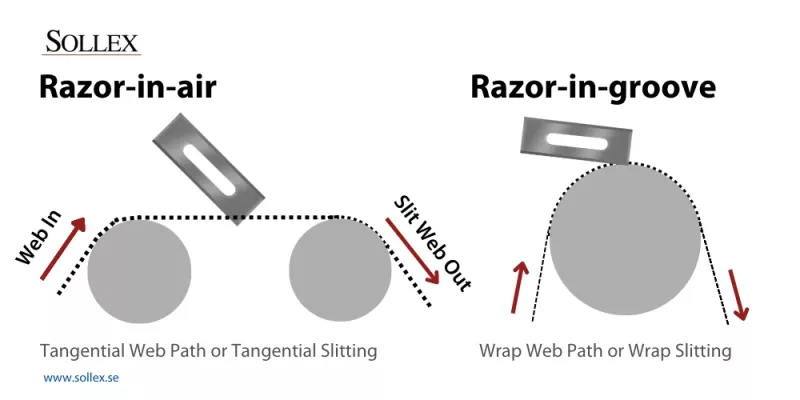
There are two main types of razor slitting: slit in the air or razor-in-air (top mounted) and slit in a grooved roll or razor-in-groove (bottom mounted). The first type requires no extra support at the slitting area and is better for slower speeds. The second one uses a roll with grooves that provide additional support at the point of slitting for higher running speeds. The web is wrapped around the roll, and the blade descends into the groove during cutting. This offers highly consistent slit depth and edge quality, although it requires that groove spacing precisely match the desired slit pattern.
The effectiveness of razor slitting also depends on how the web is supported underneath the blade. The simplest method involves tensioning the material between two idler rolls, which works well for general applications.
What are the advantages of the razor slitting method?
There are several advantages associated with the razor slitting method.
High precision | Razor slitting can produce very precise cuts with minimal waste. The blade can be positioned at a very specific angle to achieve the desired cut, allowing for greater accuracy. |
High-speed cutting | Razor slitting is a high-speed cutting method that can produce a large volume of cut material quickly and efficiently. This is especially useful for industries that require high-volume production, such as paper and plastic manufacturing. |
Minimal burrs | Because razor blades are very sharp, they produce very few burrs or jagged edges, which can reduce the amount of post-processing required after cutting. |
Versatility | Razor slitting can be used to cut a wide range of materials, including paper, plastic, rubber, textiles, and more. This makes it a versatile cutting method that can be used in a variety of industries. |
Low tooling costs | The equipment used for razor slitting is relatively simple and low-cost, which can help reduce overall production costs. |
Consistent quality | Razor slitting can produce consistent, high-quality cuts, which can improve the overall quality of the finished product. |
Overall, the razor slitting method is a highly effective cutting method that can provide numerous benefits in terms of precision, speed, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Nevertheless, the razor slitting method is not optimized to cut rigid, heavy, or extremely abrasive materials. Wrong razor blades may generate enough heat to melt film or create a bead, which is detrimental to achieving good roll edges. In contrast, shear slitting offers better performance at higher speeds and longer blade life, making it more suitable for abrasive or multi-layer materials. Besides, although the razor blades are of low cost, they need to be frequently changed to ensure a good-quality slit edge.
“On modern packaging lines, razor slitting easily runs at 200–600 m/min with consistent edge quality.”
You can also read about 13 common problems with cutting plastic film, and what you can do about them in our blog article.
The Right Blade Selection
Which blades are used for razor slitting?
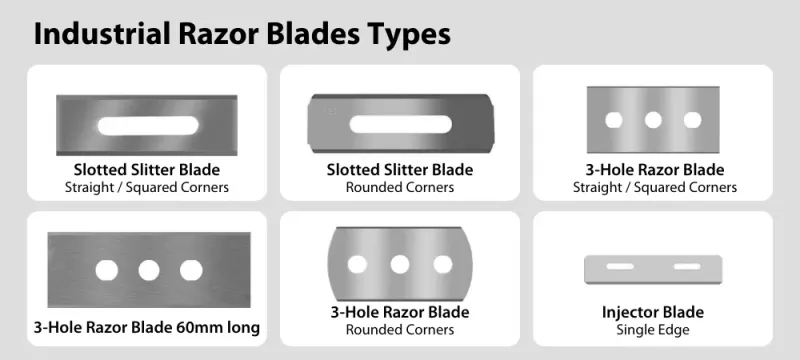
Industrial razor blades are used for razor slitting in slitter or converter machinery. These blades are thin, straight slitting blades optimized for cutting narrow strips of material. Industrial razor blades are used in various manufacturing and processing industries to cut through different materials such as plastic film and foil, stretch wrapping film and other soft materials. Industrial razor blades are typically made of high-quality steel or other durable materials, such as tungsten carbide or ceramic, that allow them to withstand heavy usage and produce precise cuts over long periods.
“In one PET label film trial, a ceramic-coated Sollex blade lasted 4 weeks versus only 3 minutes for an uncoated blade.”
Synonyms for industrial razor blade: industrial cutter blade, film slitting blade, converting blade, razor slitter, three-hole double-edge slitter, razor slitter blades with three holes, 3-slot slitter blade, 3-hole industrial razor blade, film slitting blade, rounded end 3-hole slitter, slotted blade, injector blade, slitter rewinder blade, slitting knife etc.
 Razor blades vary significantly in material and coating. High-speed steel (HSS) blades are the most commonly used due to their cost-efficiency and moderate wear resistance. For more abrasive films, such as polyethylene films, containing additives like titanium dioxide, calcium carbonate, or other mineral fillers, cemented tungsten carbide razor blades or coated options (like titanium nitride or ceramic coatings) may be necessary to reduce wear and maintain quality.
Razor blades vary significantly in material and coating. High-speed steel (HSS) blades are the most commonly used due to their cost-efficiency and moderate wear resistance. For more abrasive films, such as polyethylene films, containing additives like titanium dioxide, calcium carbonate, or other mineral fillers, cemented tungsten carbide razor blades or coated options (like titanium nitride or ceramic coatings) may be necessary to reduce wear and maintain quality.
Choosing the right razor blades makes a huge difference. We have been involved in tests where razor blades didn't last even 3 minutes. But if the same blade was coated with an additional coating, it lasted 4 weeks cutting the same material. Slitter blade life depends on several factors, including blade type, web material, speed, and slit configuration. In an optimized process, such as slitting PET label film for water bottles, one high-quality blade can last up to 300,000 linear feet. However, for abrasive materials, blade changes may be required every few hours. The right blade material and coating can extend operational uptime significantly.
What industrial razor blades are available for film and foil slitting?
 For plastic film manufacturers, we offer a number of different industrial blades:
For plastic film manufacturers, we offer a number of different industrial blades:
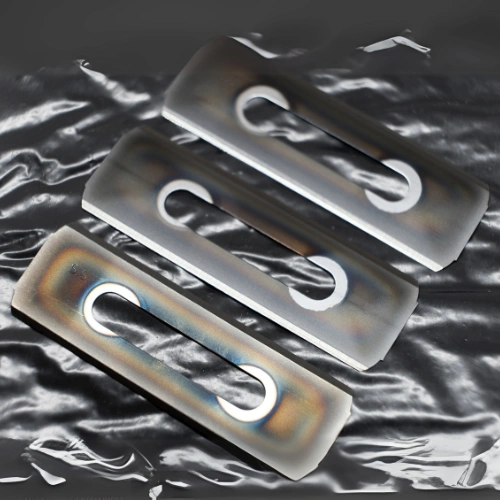
1. Slotted slitter blades. They come with straight or rounded corners. The thicknesses of such slitter blades are 0.40 mm and 0,20mm. Standard blade size is 57x19x0.40mm.
2. 3-hole industrial razor blades. Such slitting blades also come with straight and rounded corners. The blade sizes are as follows:
- 43x22x0.13 mm
- 43x22x0.15 mm
- 43x22x0.20 mm
- 43x22x0.30 mm
- 43x22x0.40 mm
- 43x22x0.40 mm
- 43x22x0.20 mm
3. Injector blades. These are small industrial blades, usually sized 38x8x0.25mm. They have 2 holes for mounting in the slitter machine.
Sollex industrial blades are available in the following materials and coatings:
- Tool Steel
- Stainless Steel
- Carbon Steel
- Solid Tungsten Carbide
- T - TiN Titanium Nitride
- Z - Zero Friction
- K - Ceramic coating
- X - Full Ceramic coating
Solid tungsten carbide slitting blades are used for heavy-duty applications, thick flexible materials, highly abrasive films, or plastic films with additives.
We use an additional coating of the cutting edge to extend blade life and reduce friction between the web material and the slitting blade. Coated cutting edges make them smoother and last longer than rough blades that are not coated.
Read more about coating for industrial razor blades here
How do coated industrial razor blades improve performance?
Ceramic-coated industrial blades are a type of razor blade that has a ceramic coating on the cutting edge. The ceramic coating is designed to improve the performance and durability of the blade.
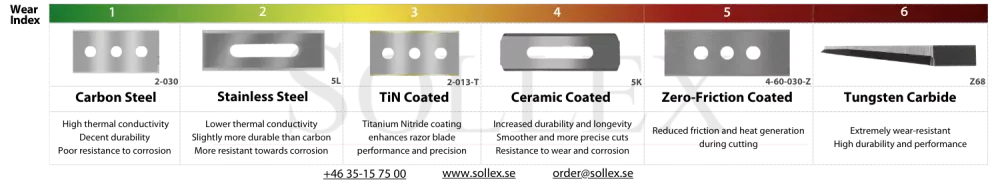
Coatings are a hard, wear-resistant material that can provide several benefits in industrial cutting applications. Some advantages of ceramic coated industrial blades include:
- Increased durability. Ceramic coatings are extremely hard and wear-resistant, which can help extend the life of the blade. Such benefits can result in fewer blade changes, reducing downtime and production costs. A longer lifespan means that the blade can cut through materials more effectively, without becoming dull or damaged as quickly.
- Reduced friction. Ceramic coatings can reduce the amount of friction between the blade and the material being cut. These properties can help prevent the material from sticking to the blade or causing heat buildup, which can result in better quality cuts and less wear and tear on the blade.
- Ceramic coatings offer enhanced resistance to corrosion. Ceramic coatings are also highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, which can help protect the blade from rust and other forms of corrosion.
Ceramic-coated industrial blades are mainly used in plastic film manufacturing, where high-precision cutting and durability is critical.
Sollex industrial blade with ceramic coating has “-K” in the end of a product article. The slitting blades are available in a range of thicknesses and designs (there are razor blades with rounded and squared corners, with slots or three holes, etc) to suit specific cutting applications and can provide a cost-effective solution for industries that require high-quality, long-lasting cutting tools.
Where can I order razor blades for slitting and converting?
Razor slitting is the simplest and most cost-effective way to cut thin films, foils, and laminates. With the right blade material, coating, and holder setup, converters can achieve clean, narrow edges at high speeds with minimal downtime. Sollex supplies a wide range of industrial razor blades, from standard carbon steel to solid tungsten carbide and advanced coatings, ensuring reliable performance in every application.
Sollex has high quality industrial razor blades for any kind of application. Our industrial-type razor blades are made of high-chromed carbon steel, stainless steel, solid tungsten carbide, and zirconia ceramic, and additional coatings of the blades are our strength.
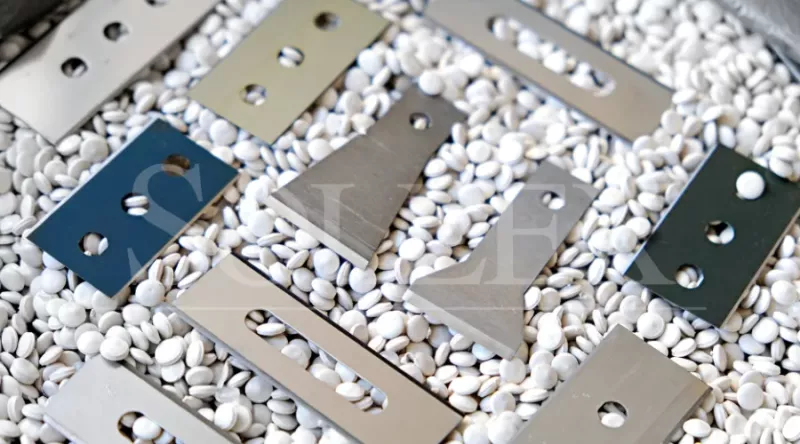

If you do not find the razor blade you are looking for, Sollex are able to manufacture industrial razor blades according to your drawing.
Download PDF with Sollex Blades for Plastic Industry
Feel free to contact us at +4635-15 75-00 if you have any questions regarding our industrial razor blades.
FAQ
Q: What is razor slitting?
A: Razor slitting is a process where a stationary razor blade cuts a moving web of thin material into narrower rolls, widely used in film, foil, and packaging converting.
Q: What are the main advantages of razor slitting?
A: Razor slitting is cost-effective, simple to set up, and ideal for thin, flexible materials. It produces precise cuts with minimal waste and burrs.
Q: Which materials are best suited for razor slitting?
A: Razor slitting is commonly used for PE, PP, PET, BOPP films, laminates, aluminum foil, and label stock. It is not ideal for thick or abrasive webs.
Q: What blade types are used in razor slitting?
A: Common types include slotted razor blades, three-hole blades, injector blades, and reinforced single-edge blades, available in different thicknesses and coatings.
Q: How do coated razor blades improve performance?
A: Coatings such as TiN, ceramic, or zero-friction extend blade life, reduce friction and buildup, and deliver cleaner edges, especially in abrasive or adhesive materials.