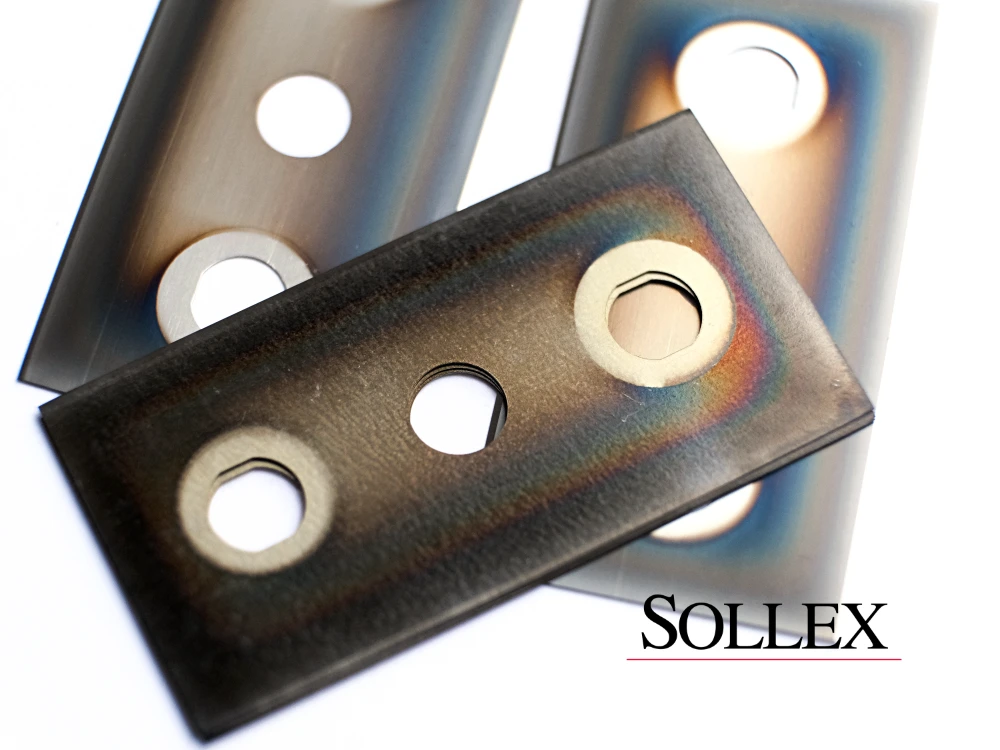
Guide to Knife & Blade Coatings
What are industrial blade coatings and why are they important? Industrial razor blades and machine knives can be enhanced with special coatings such as titanium nitride (TiN), ceramic, or zero-friction layers. These coatings increase hardness, reduce friction, improve wear resistance, and extend blade life by several times compared to uncoated steel. Coated blades cut cleaner, last longer, and reduce downtime in converting, packaging, and film slitting processes.
Table of Contents:
- About industrial blade coatings
- Coated blades vs. Uncoated blades
- Why coat SS knives
- Why coat carbon steel knives
- Sollex coated blades
- Problems coated blades solve
- Order coated industrial blades from Sollex
- FAQs
Industrial Blade Coatings for Enhanced Cutting Performance
Machine knives and slitter blades used in industrial cutting and converting processes, such as in slitter rewinder machines, are typically manufactured from steel grades, alloys, solid tungsten carbide, or, in the rarest of cases, ceramic ( zirconium dioxide ) material. Selecting the appropriate blade material, thickness, grinding, and design is critical to achieving optimal durability, controlled blade temperature, and the best cutting quality results. One of the main modern techniques for improving the properties of industrial knives is to coat them with different coatings. This article is about industrial blade coatings for enhanced cutting performance.
Read more about ceramic coating: "Ceramic Coating for Industrial Razor Blades and Machine Knives"
Read more about TiN coating: "Sollex Titanium Nitride (TiN) Coated Blades"
Read more about Zero-Friction coating: "Zero-Friction Coating for Industrial Razor Blades"
How do coated industrial blades perform compared to uncoated blades?
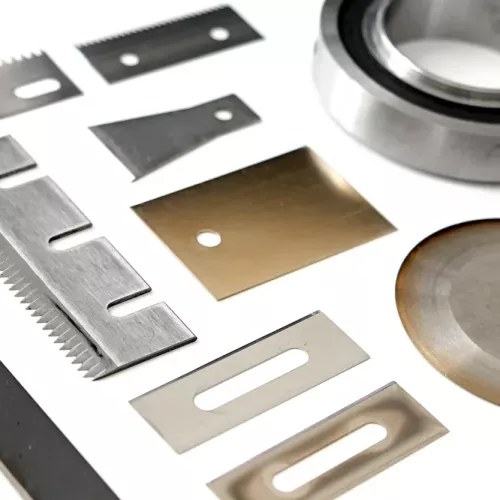 Coating significantly enhances industrial blade performance. While standard steel blades have a hardness range of approximately 45-65 HRC, coatings based on tungsten carbide can dramatically increase surface hardness to levels between 1600 and 7000 Vickers. However, hardness is only one attribute improved by coatings; blade edge topography, frictional properties, and heat conductivity are also notably optimized.
Coating significantly enhances industrial blade performance. While standard steel blades have a hardness range of approximately 45-65 HRC, coatings based on tungsten carbide can dramatically increase surface hardness to levels between 1600 and 7000 Vickers. However, hardness is only one attribute improved by coatings; blade edge topography, frictional properties, and heat conductivity are also notably optimized.
Beyond mechanical enhancements, coatings improve chemical stability, oxidation resistance, and thermal conductivity, all of which substantially influence wear resistance and operational longevity in cutting applications.
When cutting and converting abrasive materials ( e.g. PCR plastic film), uncoated slitting razor blades suffer accelerated wear, heating, necessitating frequent replacements and increased operational downtime. High-performance coatings provide the cutting edge a durable protective barrier, surface hardness, and a reduced friction coefficient when high-speed slitting.
Why coat stainless steel knives with TiN, ceramic, or DLC?
Stainless steel knives and blades have some advantages over carbon steel. They don’t rust and can be used in cutting where there’s moisture or oil. That’s why they’re often used in food, pharma, and clean environments. But stainless steel is softer (∼50 HRC) than carbon steel (∼60 HRC), so the edge wears out faster.
To fix this, the cutting edges of stainless steel knives are often coated. Coatings like titanium nitride (TiN), ceramic, or DLC make the edge harder, reduce friction, and protect it from wear. Such treatment helps the blade last longer and cuts down on problems like chipping, burrs, and dulling.
Why coat carbon steel knives used in industrial cutting?
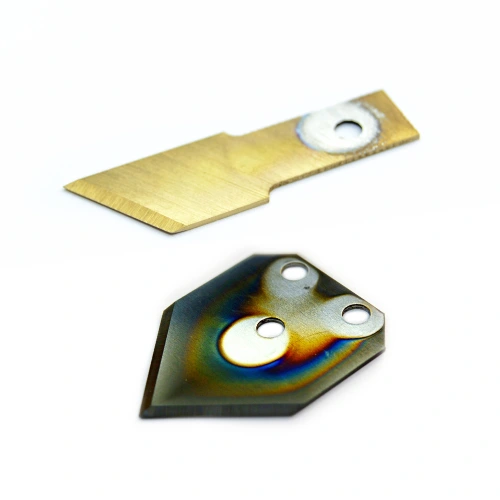 Carbon steel industrial knives have their advantages and in certain cases, they are the only right choice. As stated above, carbon steel knives are harder, and for cutting certain materials only they are the right choice. The most common machine knives, such as circular knives, top and bottom slitter knives, pelletizing, die-face cutter and granulator knives, serrated knives, and many others, are made from carbon steel like D2 and HSS M2 at Sollex. Since carbon steel knives are harder, you will get a better cutting edge on the cutting material.
Carbon steel industrial knives have their advantages and in certain cases, they are the only right choice. As stated above, carbon steel knives are harder, and for cutting certain materials only they are the right choice. The most common machine knives, such as circular knives, top and bottom slitter knives, pelletizing, die-face cutter and granulator knives, serrated knives, and many others, are made from carbon steel like D2 and HSS M2 at Sollex. Since carbon steel knives are harder, you will get a better cutting edge on the cutting material.
D2 carbon steel knives are easier to grind, while HSS M2 knives are even harder and grinding is more challenging. Another important feature of carbon steel knives is that they are much cheaper than other materials and for many businesses the price is an important factor.
However, the disadvantages of carbon steel knives are their tendency to rust and their short shelf life. Such knives need to be properly packaged and stored on the shelf. Also, due to the high density of these particular knives, they are prone to chipping and cracking at the cutting edge. To solve the above problems, carbon steel knives are coated with additional coatings. Fully coated knives are protected against rust and can be used even when cutting with moisture and abrasive materials. In addition, the wear of the cutting edge, if coated, will be reduced, and the life expectancy will be extended many times over.
If a large number of knives and blades are used in production and conversion and consumption is high, it may make sense to invest in more durable knives. Carbon steel is one solution, but better durability may be achieved with coatings or solid hard metals.
Which Sollex blades are available with coatings?
Sollex applies the advanced coating to its slitting knives, slotted razor blades, three-hole blades, injector blades, CNC knives and router bits, circular and custom-made machine knives, and even utility blades, giving converters and packaging companies an easy way to reduce downtime while keeping cuts ultra-clean and food-safe.
Blade Type | Description |
|---|---|
For film and foil slitting in high-speed industrial machines | |
Standard in packaging and converting industries | |
Compact blades for precise and delicate cuts | |
Custom knives for automated or manual cutting equipment | |
Trapezoid-shaped / hook / concave / snap-off blades for utility knives |
Below you will find the primary industrial blade coating types for Sollex's blades.
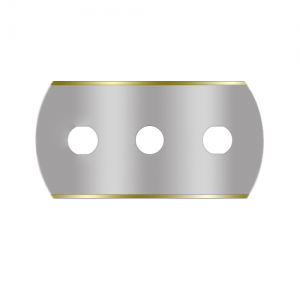
T – Titanium Nitride (TiN) Coating
TiN coating gives blades a characteristic gold edge and is widely used for slitting plastic films and foils with few additives. The titanium nitride layer increases hardness and reduces friction, which means less dust and cleaner cuts. It is FDA-approved for food contact and offers a good balance of durability, performance, and cost efficiency. TiN-coated blades are often chosen for standard high-volume film converting where reliability and cleanliness matter.
K – Ceramic Edge Coating
Ceramic edge coating is applied as a fine-grain black layer on the cutting edge, protecting blades when slitting plastic films filled with minerals such as calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) or titanium dioxide (TiO₂). These additives are abrasive and would normally wear down steel edges quickly. The ceramic coating dramatically increases wear resistance and maintains edge sharpness, which results in longer production runs, fewer blade changes, and reduced downtime. It is also FDA and EC approved for contact with food.
Z – Zero-Friction Coating
Zero-friction coating appears grey and has an extremely fine surface structure. It is designed for high-speed cutting of thin stretch films, where minimizing drag is essential. By lowering the coefficient of friction, this coating helps the blade glide smoothly through clingy, elastic films without tearing or causing heat buildup. The result is clean, precise cuts even at high web speeds. Like other Sollex coatings, zero-friction blades are FDA and EC approved for food contact.
X – Full Ceramic Coating
The X coating covers not only the edge but also the entire surface of the blade, creating a fully protected cutting tool. This full ceramic layer is especially effective for multilayer films and plastic films with aggressive additives, where both edge and blade surface are exposed to abrasive or adhesive wear. By protecting the whole blade, the X coating extends tool life significantly and keeps blades sharper over long runs. These blades are also FDA and EC approved for food contact.
C – Solid Ceramic Blades
Solid ceramic blades are made entirely of a self-grinding, heat-resistant ceramic material. They are extremely durable and maintain their sharpness even under high temperatures. Solid ceramic blades are ideal for cutting soft, flexible films such as EBA, which are prone to melting or deformation with steel blades. While ceramic is more brittle than steel, it delivers exceptional performance and longevity in applications where sharpness and thermal stability are critical.
Coating | Specification | Material to cut |
|---|---|---|
T | Titanium (TiN)-coated blades for optimal slitting performance. Gold-colored edge. The blades exhibit low friction, thereby producing less dust. Competitive durability and performance. FDA-approved. Learn more about this type of coating here in our blog. | Plastic film and foil with few additives |
K | The ceramic coating is black in color and has a fine grain structure. When cutting plastic film with additives such as chalk or titanium, the ceramic coating optimally protects the edge. The product is FDA and EC approved for contact with food. High durability and performance. Learn more about this type of coatinghere in our blog | Plastic film with e.g. calcium carbonate mineral additives |
Z | The zero-friction coating is grey in color and has an extremely fine grain structure. This coating gives minimal friction, optimal for high-speed cutting such as thin stretched film. The coating is FDA and EC approved for contact with food. High durability and performance. Learn more about this type of coatinghere in our blog | Thin stretch film |
X | Full ceramic-coated blade where the sides of the blade are also coated. FDA and EC approved for food contact. This blade offers exceptional durability when cutting materials that contain harsh additives. | Plastic film with additives, multilayer |
C | Solid ceramic coating, self-grinding and heat resistant. Ideal for high-performance requirements. The material is fragile, yet it retains its sharpness and temperature control, making it ideal for cutting soft, flexible films that are prone to melting. Extreme durability and performance. | Soft flexible film (EBA) |

Examples of Sollex blades coated with a titanium nitride coating (-T): 5T, 1-015-T, 2-020-T, 1-030-T, 9-065-T, 10PT, 9030-T, 16PT
Examples of Sollex blades coated with a ceramic coating (-K): 5K, 1-013-K, 1-020-K, 2-013-K, 2-030-K, 4-60-030-K, 635K
Examples of Sollex blades coated with a zero-friction coating (-Z): 5Z, 5LZ
Examples of Sollex blades fully coated with a ceramic coating (-X): 5X, 2-020-X, 2-030-X, 619X
Examples of Sollex blades made of ceramic material (-C): 2-013-C, 5C
It is important to keep in mind that the variety of blade coatings is due to the fact that the coatings provide different characteristics to the blades and allow them to cut different types of material. To find the right blade, it is often a challenge to test different options until the best one is found, as many other factors affect the quality of the cut (composition of the converting material and material thickness, cutting speed, blade angle, cutting method, and more).
What problems do coated blades solve in industrial converting?
Sollex coatings modify the cutting characteristics of machine knives and slitting machine blades. Thanks to our extensive experience in industrial knife development, close cooperation, and trials with our customers,  we have identified the main benefits and results from the use of coated knives in the production and converting of packaging materials :
we have identified the main benefits and results from the use of coated knives in the production and converting of packaging materials :
- Protective coatings significantly prolong blade edge life
- Certain coating textures improve the accuracy and quality of cutting
- Reduce adhesive wear
- Provide the industrial knife with good sliding qualities and a low coefficient of friction
- Prevent rust
- Expands the field of application and enables cutting of new advanced materials
- Because fewer new knives are bought and less production waste is produced, costs are decreased
- Less dust and dirt collects on the surface of coated blades and less glue when cutting adhesive materials
- When cutting plastic film at high speed, the risk of melting the cut edge is reduced
- Full-side coatings effectively manage and dissipate blade heat
Where can I order Sollex coated knives and blades?
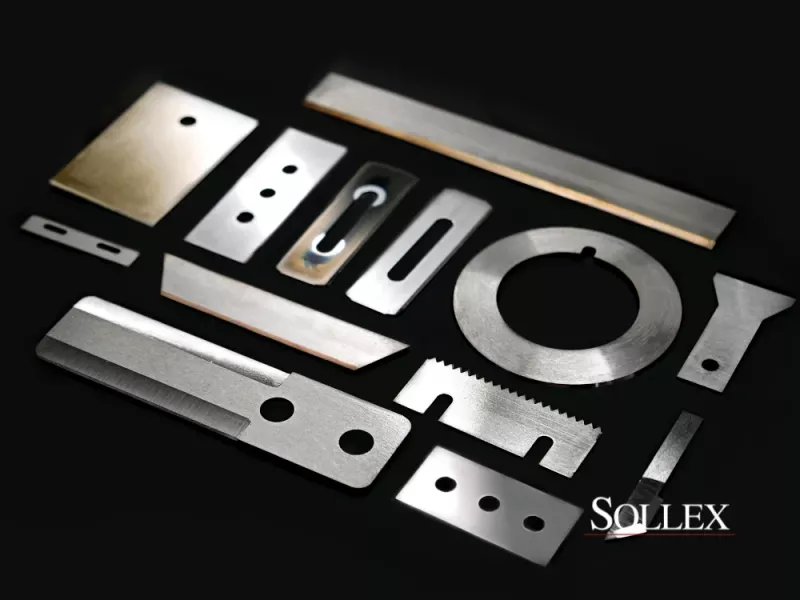
Sollex offers industrial blades coated with a precisely controlled layer developed for professional use. The coating is applied using advanced arc PVD technology and is consistently optimized for industrial applications. Customers all over the world rely on Sollex coated blades to improve output quality and reduce tooling wear in demanding industrial processes. Contact us at order@sollex.se for more information.
FAQ
Q: What are industrial blade coatings and why are they important?
A: Industrial blade coatings such as titanium nitride (TiN), ceramic, and zero-friction layers improve blade hardness, reduce friction, increase wear resistance, and significantly extend blade life. Coated blades deliver cleaner cuts, less dust, and reduced downtime in converting and slitting processes.
Q: How do coated blades perform compared to uncoated blades?
A: Coated blades outperform uncoated steel blades by offering much higher surface hardness, better heat resistance, lower friction, and longer service life. This is especially important when cutting abrasive, recycled, or high-speed plastic films.
Q: Why are stainless steel knives often coated?
A: Stainless steel knives resist corrosion but are softer than carbon steel. Applying coatings such as TiN, ceramic, or DLC increases edge hardness, reduces wear, and improves cutting performance in demanding applications.
Q: Why should carbon steel knives be coated?
A: Carbon steel knives are sharp and cost-effective but prone to rust, chipping, and short shelf life. Coating carbon steel blades protects against corrosion, reduces edge wear, and extends blade lifespan in industrial cutting.
Q: What industrial blade coatings does Sollex offer?
A: Sollex offers titanium nitride (TiN), ceramic edge coating, zero-friction coating, full ceramic coating, and solid ceramic blades. Each coating is designed for specific materials such as plastic films, multilayer films, stretch films, and abrasive compounds.
Q: What problems do coated blades solve in film slitting and converting?
A: Coated blades reduce friction, minimize dust and adhesive build-up, prevent edge melting, resist corrosion, and extend blade life. They also improve cut quality and enable stable cutting at higher production speeds.
Q: How do I choose the right blade coating for my application?
A: Blade coating selection depends on material type, additives, cutting speed, and process conditions. TiN is suitable for clean films, ceramic for filled or abrasive films, zero-friction for thin stretch films, and full ceramic or solid ceramic for aggressive or multilayer materials.
Q: Where can I order coated industrial blades from Sollex?
A: Sollex supplies coated industrial razor blades and machine knives using advanced PVD coating technology. Orders and technical support are available via order@sollex.se.